-
111

- Distributional and hierarchical reinforcement learning for physical systems with noisy state observations and exogenous
- Distributional and hierarchical reinforcement learning for physical systems with noisy state observations and exogenous perturbations Professor Jongeun Choi's research team in the Department of Mechanical Engineering conducted a study on algorithm robust to noise and extrinsic perturbation by combining the advantages of distributed reinforcement learning and hierarchical reinforcement learning. This study was published in the journal of 'Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence' (Impact Factor: 8.000, top 5.55%, Volume 123) in May 2023. In this paper, our approach demonstrates promising results in handling uncertainties caused by noise and perturbations for challenging sparse-reward tasks, and could potentially pave the way for the development of more robust and effective reinforcement learning algorithms in real physical systems. The link: doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2023.106465
- 기계공학부 2023.08.10
-
110
- Physics-added neural networks: An image-based deep learning for material printing system (2023.07.05)
- Physics-added neural networks: An image-based deep learning for material printing system Professor Joon Sang Lee's the division of inkjet printing solution research team in the Department of Mechanical Engineering proposed the physics-added neural networks (PANNs) to improve training efficiency and accuracy by adding physics in inkjet printing system. The research paper is published in the journal of 'Additive Manufacturing' (Impact factor: 13.632, top 0.98%, Volume 73) in July 2023. In this paper, PANNs was adopted in inkjet printing optimization where thermal effect is applied. The link: https://authors.elsevier.com/a/1hJls7tcTWlNh0, DOI: doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2023.103668
- 기계공학부 2023.07.19
-
109
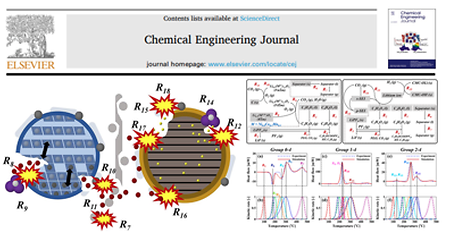
- Improving EV safety by identifying thermal runaway mechanisms in high nickel-based Lithium-ion batteries (2023.06.27)
- Improving EV safety by identifying thermal runaway mechanisms in high nickel-based Lithium-ion batteries A research team led by Professor Jongsup Hong of the Department of Mechanical Engineering has developed an original technology to improve the safety of lithium-ion batteries based on high-nickel cathode materials, which have been receiving increasing attention for improving the range of electric vehicles amid the rapid transition to vehicle electrification and the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. The research was published in the Chemical Engineering Journal (Impact Factor: 15.1, Top 3.2%, Volume 471), a top journal in the field of thermal and reaction engineering, in July 2023. In this paper, we identified the thermal runaway mechanism of lithium-ion batteries based on high-nickel cathode materials by considering the phenomena occurring at each electrode individually through a combination experiment between materials, and developed a reliable model to increase the utilization of the mechanism, paving the way for improving the safety of electric vehicles. The link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.144434
- 기계공학부 2023.07.19
-
108
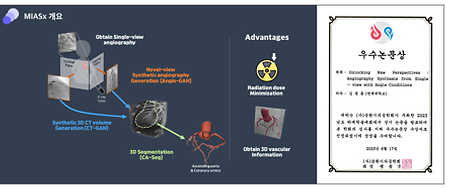
- Unlocking New Perspectives: Angiography Synthesis from Single-view with Angle Conditions (2023.06.17)
- Unlocking New Perspectives: Angiography Synthesis from Single-view with Angle Conditions Professor Joon Sang Lee's research team from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at Yonsei University has received an outstanding paper award at the 2023 Summer Conference of the Biomedical Engineering Society for Circulation for their research titled "Unlocking New Perspectives Angiography Synthesis from Single-view with Angle Conditions." In this study, they proposed a generative artificial intelligence model that generates novel-view images from single-view image obtained from coronary angiography, which is used for the diagnosis of coronary artery disease. Through this approach, it is expected that the number of angiography scanning can be reduced, and the radiation dose exposed to patients can be decreased, thereby contributing to the improvement of the medical environment. The link: https://mfdl.yonsei.ac.kr/home
- 기계공학부 2023.07.19
-
107
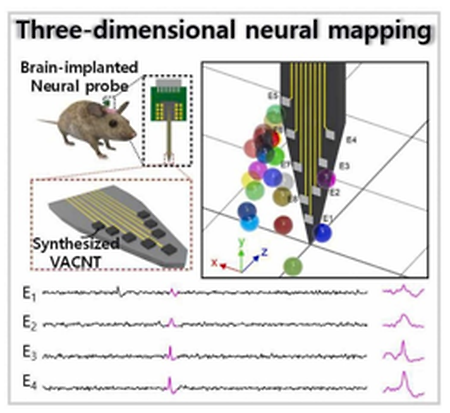
- Development of neural probe electrodes with low-impedance enable of three-dimensional neural signal mapping (2023.06.09)
- Development of neural probe electrodes with low-impedance enable of three-dimensional neural signal mapping Professor Jongbaeg Kim's research team in the Department of Mechanical Engineering and a research team at Korea University School of Medicine conducted a study on "Neural probe electrodes enabling to measure tiny neural signals." This study was published in the journal "Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical (Impact Factor: 8.4, top 1.58%)". Measuring complex brain nerve activity is important to overcome brain nerve diseases, such as dementia and Parkinson's disease. The probe-type electrode developed by this research team has very low impedance, so it can measure even tiny nerve signals, which were difficult with existing electrodes. Notably, this neural probe can be obtained three-dimensional nerve distribution information. The link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2023.134124
- 기계공학부 2023.07.19
-
106
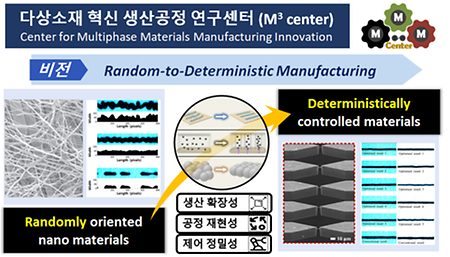
- The Department of Mechanical Engineering at Yonsei University has been selected as the host institution for the leading
- The Department of Mechanical Engineering at Yonsei University has been selected as the host institution for the leading research center, sponsored by the Ministry of Science and ICT The Department of Mechanical Engineering at Yonsei University has been selected as the host research institution for the Engineering Research Center (ERC), granted by the Ministry of Science and ICT in 2023. The "Center for Multiphase Materials Manufacturing Innovation Research Center (M3 Center)" consists of 11 researchers, including Professor Jongbaeg Kim in the Department of Mechanical Engineering at Yonsei University as the center leader. This Center aims to establish a precision-controlled manufacturing platform based on multiphase materials with outstanding characteristics and lead innovation in producing advanced application components. The engineering research center will receive a total of 13.5 billion won in government support over 7 years and has contracted a commitment of 1.091 billion won in research funding from 10 industrial companies, including Hyundai Motors and Samsung Display. The link: https://www.msit.go.kr/bbs/view.do?sCode=user&mId=113&mPid=238&pageIndex=10&bbsSeqNo=94&nttSeqNo=3183180&searchOpt=ALL&searchTxt=
- 기계공학부 2023.07.19
-
105
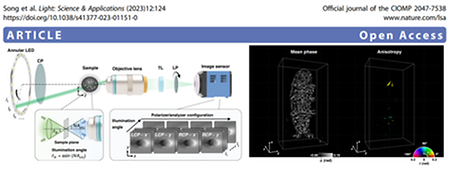
- Polarization-sensitive intensity diffraction tomography (2023.05.18)
- Polarization-sensitive intensity diffraction tomography Professor Chulmin Joo's research team at the Department of Mechanical Engineering introduced a computational microscopy platform capable of producing tomographic birefringence images of optically anisotropic materials. Existing birefringence tomography methods mostly operate on interferometric setups, along with single-scattering models, which limits high-fidelity reconstruction of birefringence information of complex and multiple-scattering objects. The researchers developed a vectorial multiple scattering model as a method to analyze the propagation of light in multiple scattering birefringent objects, and combined it with non-interferometric microscopy setup to enable three-dimensional birefringence imaging of multiple-scattering anisotropic materials. This research was published on May 18, 2023 in the journal Light: Science & Applications (IF 20.257). The link: doi.org/10.1038/s41377-023-01151-0
- 기계공학부 2023.07.19
-
104
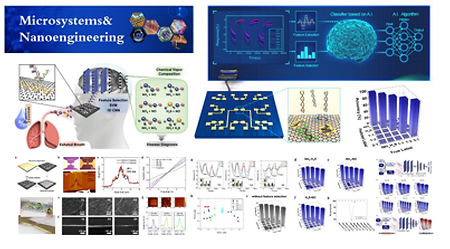
- Development of human expiratory gas biomarker detection and artificial intelligence discrimination of mixed state
- Development of human expiratory gas biomarker detection and artificial intelligence discrimination of mixed state Department of Mechanical Engineering Professor Seong Chan Jun's research team and Professor Jongeun Choi's research team collaborated to conduct a study on the topic of 'Sensing the mixed state of disease biomarker gases that can be emitted through human exhaled gases and identifying artificial intelligence'. The joint research team developed an ssDNA-functionalized graphene-based sensor array that can detect mixed gases by direct adsorption method, and developed two artificial intelligence models that can discriminate the mixed state, and verified the discrimination performance. The results of this research were published as a thesis and published in the international journal 'Microsystems&Nanoengineering' (Impact Factor: 8.006). The link: doi.org/10.1038/s41378-023-00499-y
- 기계공학부 2023.07.19
-
103
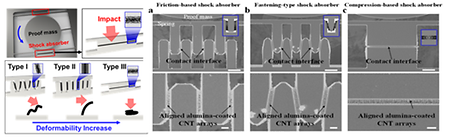
- Integration of Mechanically Resilient, Alumina-Reinforced Carbon Nanotube Arrays for In-Plane Shock Absorption in Microm
- Integration of Mechanically Resilient, Alumina-Reinforced Carbon Nanotube Arrays for In-Plane Shock Absorption in Micromechanical Devices The research team led by Professor Jongbaeg Kim, including co-first authors Research Professor Eunhwan Jo and master's researcher Hojoon Lee, has conducted a study on ceramic-reinforced carbon nanotube-based shock absorbers. The study focuses on the usage in the field of micro/nano electromechanical systems (MEMS/NEMS) and has been approved for publication in an international journal 'Microsystems & Nanoengineering' which has Impact Factor of 8.006, placing it in the top 6.25% in the field of Instrument & Instrumentation. The researchers integrated vertically aligned nanotube bundles into MEMS to enhance the shock capability of microstructures against impacts. This advancement is particularly significant as it addresses the vulnerability of subminiature devices to impact. This study is collaborated with Harvard Medical School in the United States to strengthen the study's potential impact. It's worth mentioning that this study received support from the 'Midcareer Research Grant' funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, leaded by Prof. Jongbaeg Kim as a project investigator.
- 기계공학부 2023.05.25
-
102
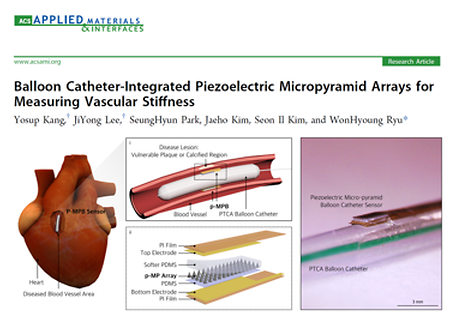
- Development of Piezoelectric Micropyramid Balloon Catheter Sensor for Measuring Vascular Stiffness (2023.04.03)
- Development of Piezoelectric Micropyramid Balloon Catheter Sensor for Measuring Vascular Stiffness The research team, led by Professor WonHyoung Ryu from the Department of Mechanical Engineering (co-first authors of this study are Yosup Kang and JiYong Lee), has developed a piezoelectric balloon catheter sensor using a micro-pyramid structure composed of flexible piezoelectric nanocomposite materials. It has been demonstrated that this piezoelectric balloon catheter sensor can be utilized for the diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases by directly measuring the mechanical strength of lesion areas within blood vessels. This research has been published in the renowned international academic journal 'ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces' (Impact Factor: 10.383) in April 2023. The link: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acsami.3c00700
- 기계공학부 2023.05.25