-
161

- Dr.Yang appointed as Assistant Professor at Chung-Ang University
- Dr.Yang appointed as Assistant Professor at Chung-Ang University Dr.Yang, who received her Ph.D. in August 2018 and worked as a postdoctoral researcher in the laboratory of Professor Wonhyung Ryu of the Department of Mechanical Engineering, was appointed as an assistant professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering at Chung-Ang University in September. While working as a postdoctoral researcher in the Department of Mechanical Engineering at Yonsei university, Dr.Yang published top-level SCI papers on research on nano-rapid prototyping technology and applications of polymer composite materials using a thermal drawing process and research on drug delivery devices based on microstructures. After that, she was selected for the Korea Postdoctoral Training Program of NRF and worked as a researcher in the laboratory of Professor John Rogers at Northwestern University in the U.S. There, she participated as the main author or co-author in numerous papers including the Science on various research topics including the design and fabrication of wearable sensors using 3D printing.
- 기계공학부 2024.10.08
-
160
- Honored with Two Outstanding Presentation Awards at the International Conference on Precision Engineering and Sustainabl
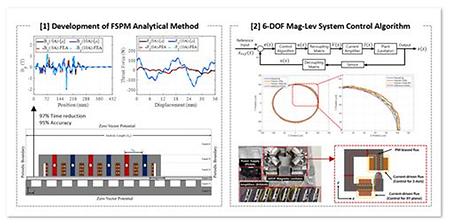
- Honored with Two Outstanding Presentation Awards at the International Conference on Precision Engineering and Sustainable Manufacturing 2024 (PRESM 2024) The research team, led by Professor Jun Young Yoon from the Department of Mechanical Engineering (Hyo Geon Lee, Ph.D. candidate, and Chang Hwan Kim, M.S. candidate) has been recognized for their outstanding achievements in two research topics at the International Conference on Precision Engineering and Sustainable Manufacturing held in July 2024. Hyo Geon Lee developed a high-speed, high-accuracy motor analysis technique based on the magnetic permeability matrix for a magnetic flux-switching motor using transverse permanent magnets. This method achieved higher analytical precision compared to existing magnetic circuit-based methods and demonstrated its potential as a promising method in the early stages of design optimization. Chang Hwan Kim presented a control algorithm for maintaining the dynamic performance of a 6-DOF magnetic levitation system, considering changes in payload. As the payload changes, the dynamic characteristics of the system also change, resulting in the degradation of control performance. To address this, he designed a mass-compensator and validated its efficacy by comparing the control performance under varying payloads. The two studies were selected for the 'Outstanding Presentation Award,' given to only 22 out of 305 presentations. The link: https://2024.presm.org/
- 기계공학부 2024.10.08
-
159
- Ultra-low-energy operation of electromagnetic bi-stable actuator under restricted energy supply
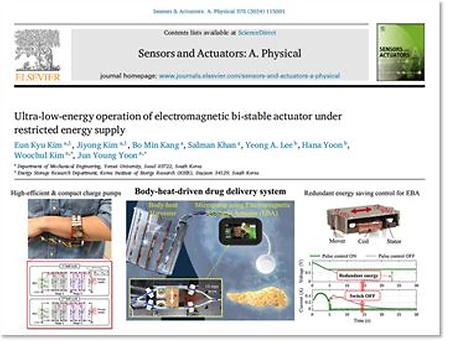
- Ultra-low-energy operation of electromagnetic bi-stable actuator under restricted energy supply The research team, co-led by Professor Jun Young Yoon and Woochul Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering (co-first authors of this study are Eun Kyu Kim and Jiyong Kim), has developed ultra-low-energy operation method of an electromagnetic bi-stable actuator under restricted energy supply. Utilizing the proposed high-efficient voltage step-up converter and the energy-saving actuator control method, the research team has demonstrated the energy-efficient operation of the bi-stable actuator which is solely driven by body-heat energy recovery, showing significant potential for self-powered wearable healthcare applications. This research has been accepted in the renowned international academic journal 'Sensors and Actuators:A. Physical' in August 2024. The link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2024.115801
- 기계공학부 2024.10.08
-
158
- Single-shot calibration method based on Fourier transforprofilometry
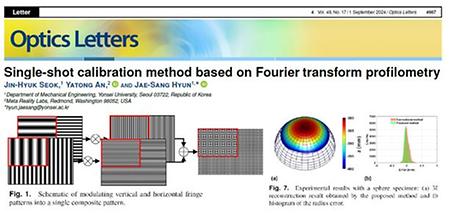
- Single-shot calibration method based on Fourier transforprofilometry The research team led by Professor Jae-Sang Hyun from the Department of Mechanical Engineering (with first author Seok Jin-Hyuk, integrated course) conducted joint research with Meta Reality Labs and successfully developed a single composite pattern for 3D camera calibration. Their research findings were published in the journal 'Optics Letters.' In this study, a composite pattern based on Fourier transform was developed to simplify the calibration of the 3D shape reconstruction system required during the eye-tracking process. The link: doi.org/10.1364/OL.535338
- 기계공학부 2024.10.08
-
157
- Novel approach for fast structured light framework using deep learning
- Novel approach for fast structured light framework using deep learning The research team led by Professor Jae-Sang Hyun from the Department of Mechanical Engineering (with first author Won-Hoe Kim, integrated course) conducted joint research with Purdue University and has developed an 'Novel approach for fast structured light framework using deep learning.' Their research findings were published in the prestigious journal 'Image and Vision Computing,' a leading publication in the field of computer vision. Unlike existing structured light methods that combine multiple images for reconstruction, this study utilizes deep learning to enable 3D reconstruction using only two images, maximizing speed. Additionally, training data necessary for framework development was generated and validated through a virtual environment, and an algorithm was developed to minimize errors, allowing for accurate and rapid 3D reconstruction. The link: doi.org/10.1016/j.imavis.2024.105204
- 기계공학부 2024.10.08
-
156
- Development of Microfluidics-based condensation bioaerosol sampler for multipoint airborne virus monitoring
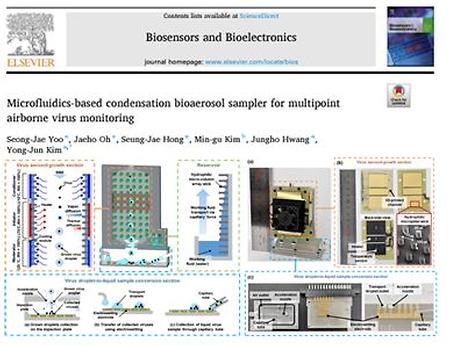
- Development of Microfluidics-based condensation bioaerosol sampler for multipoint airborne virus monitoring Professor Yongjun Kim's research team from the Department of Mechanical Engineering (1st author of this study is Seong-Jae Yoo, and corresponding author is Professor Yong-Jun Kim) has developed and manufactured a microfluidic-based condensation growth bioaerosol sampler (MCBS). The microfluidic-based condensation growth bioaerosol sampler (MCBS) is a device that grows, captures, and transports viruses by using condensation nucleus growth technique and electrowetting technology. It has been demonstrated that MCBS can concentrate airborne viruses into a small liquid sample of tens of microliters, and obtain virus liquid samples with 89.9-times higher concentration than commercial sampler. This research has been published in renowned international academic journal 'Biosensors and Bioelectronics' (Impact Factor: 10.7) in April 2024. The link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2024.116658
- 기계공학부 2024.10.08
-
155
- Designing the Solid Oxide Electrochemical Cell for Superior Thermal Shock Resistance
- Designing the Solid Oxide Electrochemical Cell for Superior Thermal Shock Resistance Professor Hong Jong-seop of Yonsei University, Professor Joo Jong-hoon of GIST, and Dr. Shin Tae-ho of the Korea Institute of Ceramic Engineering and Technology collaborated to develop a solid oxide fuel cell technology that operates at temperatures exceeding 900°C within three seconds. This newly developed technology is expected to be utilized in power generation devices that require rapid activation, such as auxiliary power sources for mobile devices like drones. Solid oxide fuel cells, made from ceramic materials, have the disadvantage of being vulnerable to thermal shock due to their low thermal conductivity and high elastic modulus. To address this, the team designed a fuel cell with high resistance to thermal shock by simulating and optimizing the electrolyte material and thickness characteristics of the solid oxide fuel cell, based on an understanding of thermal stress. The developed solid oxide fuel cell operated without cracking or breaking, even at a rapid heating rate that reached over 900°C within three seconds. Furthermore, it demonstrated high stability over more than 100 thermal shock cycles and was confirmed to operate even in extreme conditions where it reached 1000°C in under a second. This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea's Original Research and Development Program, the Future Hydrogen Innovation Technology Development Project, and the Leading Research Center Program. It was published online in the prestigious international journal ACS Energy Letters (IF: 18) on July 24, 2024. The link: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acsenergylett.4c01523 https://science.ytn.co.kr/program/view.php?mcd=0082&key=202408081610302635
- 기계공학부 2024.10.08
-
154

- Mechanical Eng & Electrical and Electronic Eng joint Workshop on Computational Imaging and Microscopy
- Mechanical Eng & Electrical and Electronic Eng joint Workshop on Computational Imaging and Microscopy Professor Chulmin Joo from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Seung Ah Lee from the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, hosted the "Computational Imaging and Microscopy Workshop 2024" on August 9, 2024, at the Jake Lah Hall in Baekyang Nuri, Yonsei University. This event was jointly organized by the BK21 groups of the Departments of Mechanical Engineering and Electrical and Electronic Engineering at Yonsei University. The workshop aimed to share and discuss the latest trends in computational imaging and microscopy for undergraduate and graduate students from the College of Engineering. The event featured distinguished international speakers from the field of computational optics, including Professor Chao Zuo from Nanjing University, Professor Jiamin Wu from Tsinghua University, Professor Takuro Ideguchi from the University of Tokyo, and Dr. Changwon Jang from Meta. The workshop covered six topics: ▲Computational Phase Imaging for Label-free 3D Microscopy, ▲Mesoscale Intravital Fluorescence Microscopy, ▲Mid-infrared Photothermal Quantitative Phase Microscopy for Live-cell Imaging, ▲ Computational Optics for AR/VR, ▲Quasi-calibration Method for Structured Light 3D Imaging Systems with an Auxiliary Camera, and ▲Lensless Computational Cameras for Smart Imaging. The event was attended by approximately 60 participants.
- 기계공학부 2024.08.20
-
153
- Yonsei University-Korea University-Waseda University-Keio University 4-University Graduate School of Mechanical Engineer
- Yonsei University-Korea University-Waseda University-Keio University 4-University Graduate School of Mechanical Engineering Workshop Held A graduate workshop involving the Mechanical Engineering departments of Yonsei University, Korea University, Waseda University, and Keio University was held on August 7, 2024, at Korea University's Anam Campus. The workshop brought together 9 faculty members and approximately 30 graduate students from the four universities to share their research and explore opportunities for collaborative projects. The event began with research presentations from the participating professors, followed by poster presentations by the graduate students. Key presentations included topics such as ▲A microfluidic chip-based approach for modeling the sensory innervated epidermal layer ▲The effect of Li-TFSI and SBS Block Copolymer Additives on the Electrical and Mechanical Properties of P3HT Films ▲A triaxial force plate with prism imaging and sampling moiré method ▲Membrane deployment using hyper-elastic wires.
- 기계공학부 2024.08.12
-
152
- Study on improving friction stir machining conditions of aluminum alloy 2024 reinforced with silicon carbide particles
- Study on improving friction stir machining conditions of aluminum alloy 2024 reinforced with silicon carbide particles Dr. Muhammad Nasir Bashir From MFDL lab conducted a research study on "Optimizing friction stir processing parameters for aluminium alloy 2024 reinforced with SiC particles: A taguchi approach of investigation" This study was published in Journal of Materials Research and Technology (Impact factor 6.2, top 6.3% volume 30). The study's results indicate that the optimal welding rotational speed of 1000 rpm significantly impacts the microstructure, wear rate, and microhardness. Specifically, it was observed that the stirred zone exhibited enhanced wear resistance compared to other zones. The study’s findings revealed that after implementing friction stir processing (FSP), a well-defined shear zone was observed on the advancing side of the stir zone.
- 기계공학부 2024.08.02